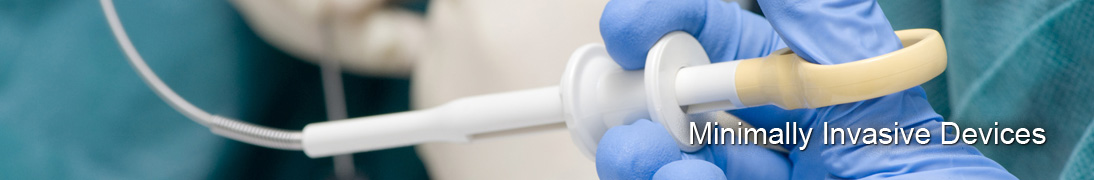
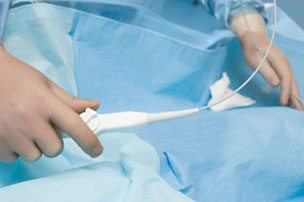
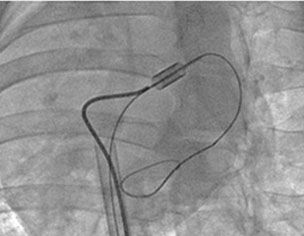
Left atrial appendage isolationThe most debilitating consequence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is stroke. Current clinical AF therapy is based on the use of blood thinners. This therapy is complicated by inherent dosing complications and patient lifestyle restrictions. In addition, many patients continue to have a significant risk of debilitating stroke despite blood thinner treatment. As an alternative treatment to augment and reduce the use of blood thinners, Ension has developed a minimally invasive tool to eliminate the risk of stroke in AF patients. This device applies a snare to the base of the left atrial appendage, a protrusion of the left atrium that has been shown to be the focus of up to 90% of stroke-causing blood clots.
Endovascular surgeryEnsion has developed enabling technologies for transcatheter correction of cardiac defects as an alternative to currently available implant-based therapies. Remote suture delivery and intracardiac patch delivery for repair of atrial septal defect (ASD) and patent foramen ovale (PFO) have been developed and demonstrated in vivo. Such technologies can more closely replicate open-chest surgical corrections than device implants for ASD and PFO though use of less material and rigid structures that historically pose a significant risk of device-related puncture or erosion. Furthermore, the transcatheter approach can obviate the need for open-chest procedures and cardiopulmonary bypass support.
Pericardial accessThe pericardial space is increasingly being used as a platform for surgical corrections, pacer lead placement, and delivery of therapeutics. Ension is developing subxyphoid-based pericardia access technology to enable safe and reliable for related emerging therapies.
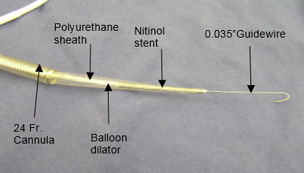
Expandable cannula for ECLSWidespread adoption of advanced life support tools such as emergency cardiopulmonary bypass and induced hypothermia has been limited by the inability to rapidly access the collapsed vasculature of a patient during cardiac arrest. Currently, a surgical cut-down procedure is needed to access the necessary vessels. The cut-down procedure is time consuming and presents a significant limitation to efficient cannulation. Stepwise dilators have been used in attempts to place large cannulae using standard over the wire techniques (i.e. Seldinger); however, their use increases cannulation time and causes trauma to the skin, tissues and vessels. Ension has developed a novel, expandable cannula that provides rapid vascular access and expand into a large bore cannula. A key facet of this effort is that the expandable cannula design allows use of the Seldinger technique and ultrasound guidance - both standards of care for catheter placement - without requiring the use of dilators. The allows a reduction typical cannulation time from 20 minutes to 5 minutes.
|
|